8 Add code coverage badge to your GitHub Repository.
In this article we will learn how to add code coverage badge to your GitHub repository.
8.1 Codecov.io
Create an account at https://about.codecov.io/ , sign up with your GitHub account if you don’t have an account already. Codecov is a popular tool for measuring and visualizing code coverage in software projects. It integrates with GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and other CI/CD systems to provide insights into how much of your code is tested by your test suite.
You can sync your private Github repositories on codecov platform to get started. If you want to add code coverage badge to a repository which is part of an organization (like PIP-Technical-Team, GPID-WB etc) then you need to be an admin of that organization. Admin role is needed because to sync the communication between Codecov.io with GitHub we need to generate a token which can only be done by admins.
Once your repo is synced with codecov and you can see it there click on Configure to start the process. As an example it should give you this screen
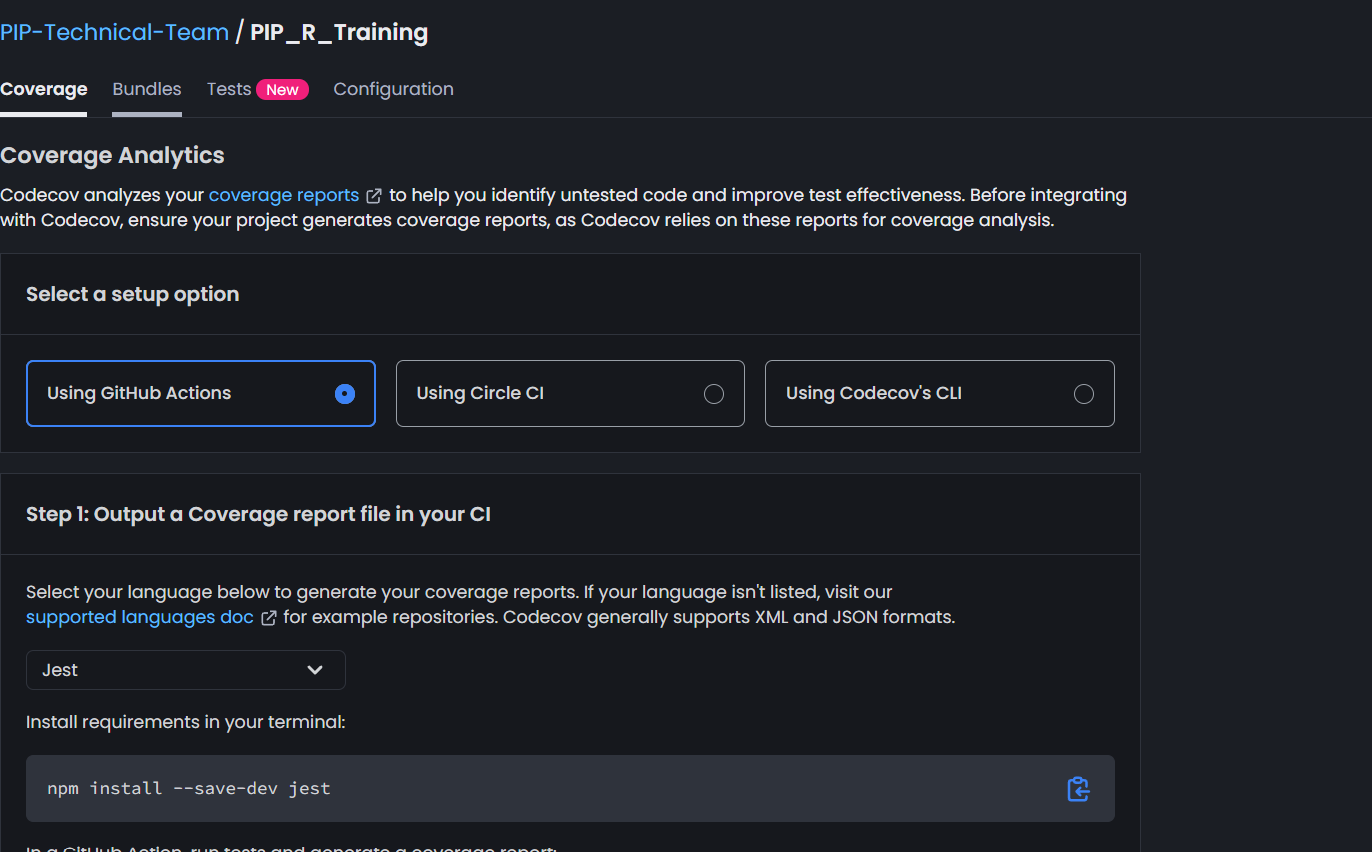
If you scroll below it will ask you to generate a repository secret, click on that to get a unique token for your repository and copy it.
You can ignore rest of the steps mentioned on that page since those are very generic language agnostic steps and since we want to setup this for R packages, we have a better option which I will share below.
8.2 GitHub
Now, moving to GitHub go to your repository. Click on Settings -> Secrets and Variables -> Actions -> Repository Secrets add the new token with name
CODECOV_TOKENand copy the token value which was generated in the previous step.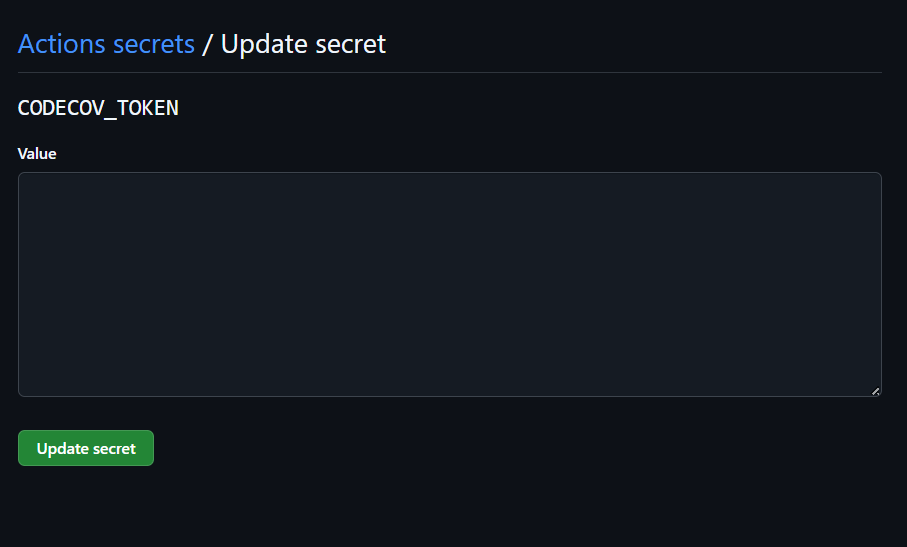
Next, we are going to setup GitHub Action to run and calculate code coverage after every push. The calculated coverage report would be uploaded on codecov.io and would be visible on their dashboard.
Additionally, I also added a possibility to run
R CMD CHECKafter every push.R CMD checkis a tool that runs a series of automated checks on an R package to ensure it’s correctly structured, documented, and error-free. It helps catch issues in code, tests, and documentation before sharing or submitting to CRAN. So it is like an additional validation that we have on our code.The new workflow file looks like below
name: R-CMD-check and Codecov on: push: branches: [master] pull_request: branches: [master] jobs: R-CMD-check: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - name: Checkout repository uses: actions/checkout@v4 - name: Set up R uses: r-lib/actions/setup-r@v2 - name: Set up pandoc uses: r-lib/actions/setup-pandoc@v2 - name: Install dependencies run: | install.packages(c("remotes", "rcmdcheck", "covr")) remotes::install_deps(dependencies = TRUE) shell: Rscript {0} - name: Run R CMD check run: | rcmdcheck::rcmdcheck(args = "--no-manual", error_on = "warning") shell: Rscript {0} - name: Run test coverage run: | covr::codecov() shell: Rscript {0} env: CODECOV_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}This file is self explanatory but briefly, it checks out the repository that we want to run our action on, sets up R to run
R CMD CHECKand finally generate code coverage report and upload it to codecov.io .One tip that I can share is to check if this workflow file works on your local branch before running on
masterbranch. To do that you should temporarily enable the workflow file to run on your local branch. This can be done as below -on: push: branches: [master, your-branch]where
your-branchis the name of the local branch that you want to run the workflow for. Once you have verified that everything works as expected in the local branch, you can removeyour-branchfrom the list again.Once the workflow runs successfully the dashboard on codecov.io should be updated and you should see something like this
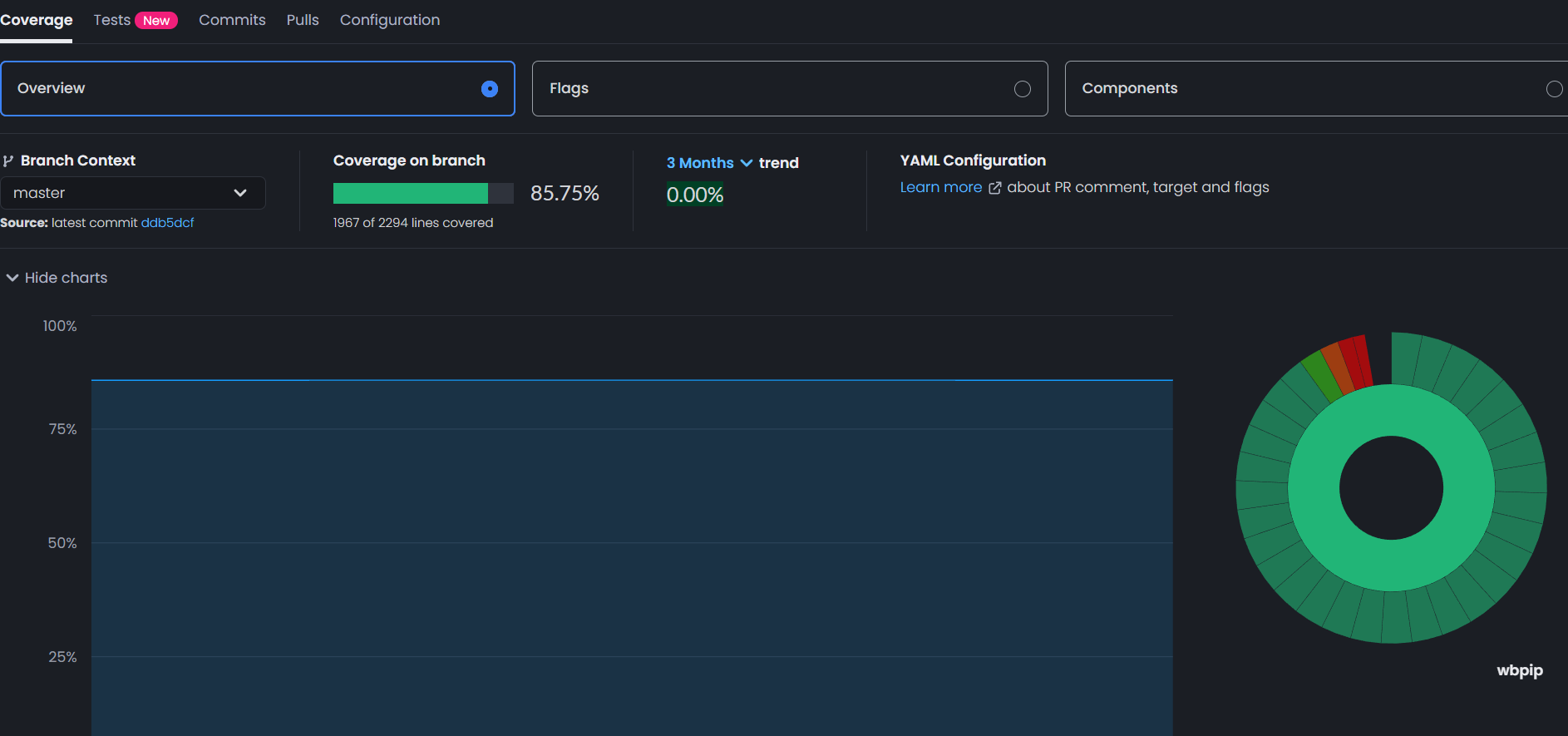
Every time a push or PR is made to
masterthe dashboard will be updated with latest data.